
Insights

Humans and Robots are Fusing Into the Workforce of the Future
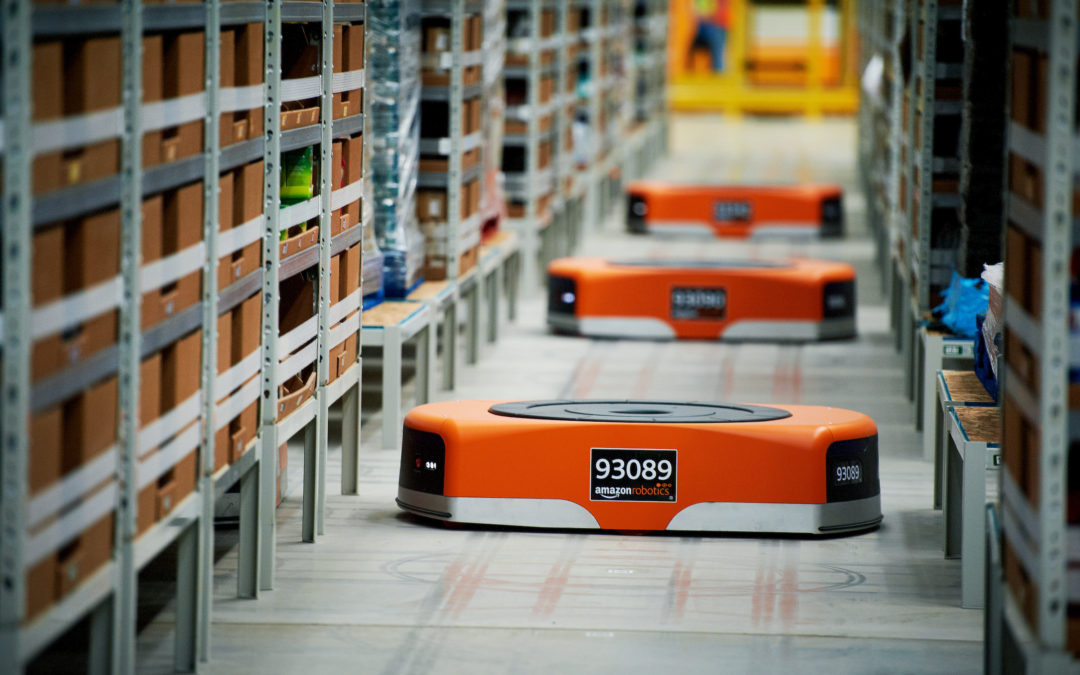
More than 300 million square feet of new warehouse and fulfillment space is needed in the US to support e-commerce. Amazon is addressing this issue with huge (3 million+ square feet) robotic fulfilment centers. These multi-level centers where humans and robots work together are springing up around the country.
Seen from above, the scale of the system is dizzying. Humans scan a package’s barcode under a red laser dot, and place it on one of hundreds of orange robots. The bot zips off, bound for one of many rectangular holes in the floor corresponding to zip codes. When it gets there, the bot engages its own little conveyor belt, sliding the package off its back and down a chute to the floor below, where it can be loaded onto a truck for delivery https://www.cnbc.com/2021/06/13/amazon-details-new-warehouse-robots-ernie-and-bert.html.
Amazon needs this robotic system to supercharge its order fulfillment process and make same-day delivery a widespread reality. Humans and robots are fusing into a cohesive workforce, one that promises to harness the unique skills of both parties.
While the introduction of robots to the workplace often raises questions about whether human jobs will be replaced, Amazon indicates that they allow workers to focus on tasks that most need their attention while minimizing their potential for injury. Also, many technical jobs at Amazon have been added to manage and improve the robotic technology. In reality, Amazon has added over a million high paying jobs around the world since it began using robotics. Amazon indicates that in the not too distant future, robotic vehicles will actually deliver packages directly to customers. This delivery system is currently under development in Finland https://www.cnbc.com/2021/07/01/amazon-plans-to-build-scout-delivery-robot-tech-in-finland.html.
Collaboration between humans and automation is the future — it will result in safer operations and higher paying technical jobs of the future.

Ants Provide The Solution To Supply Chain Chaos
Global supply chains that were broken by the pandemic are still in chaos. These problems will be with us for a while, because of market imbalances and because the just-in-time global outsourcing model no longer works for most companies and their customers.
Ants use a structured and decentralized approach to find the shortest path between food and nest. Moreover, they dynamically adjust if obstacles appear en route. Each ant makes its own decisions while staying in active communication with fellow ants. Ant colonies have scouts that examine the environment around the nest and leave scents to mark the route they took. The scout who finds the shortest way to the food source is the first one to return to the group. Other ants take notice, adapt, and follow the more efficient route. Ant behavior, honed over billions of years, is a potential key to solving today’s supply chain problems.
There are many dynamically moving parts in every supply chain. For each part, there is a business process, a large amount of data, communication protocols and decisions to be made that can impact the entire operation of the supply chain. A decision made at a functional or physical node can have significant impact on all the other nodes as well as the whole performance of the system.
Modern supply chains require a system of distributed “ants” or robotic and automated processes that can detect relevant issues and make decisions that impact the rest of the system. In other words, to maximize the performance of modern supply chains and avoid disruptions, distributed and dynamic systems similar to how ants operate, are needed.
Distributed approaches have advantages of scalability and intelligence, dynamically changing and expanding as the physical world changes. Such approaches are a major improvement to most current supply chains which are big, centralized, distant, inefficient and suffer from data and decision latency.
Nature has a lot to offer companies when it comes to optimization and efficient systems. In nature, survival is often dependent on utilizing highly optimized processes and systems. When it comes to supply chains, survival can also be dependent on implementing the best approaches and systems.

Extended Supply Chains Are Risky
Morgan Stanley recently released a note on Tesla’s future capacity and growth. The note discussed key drivers that would further Tesla’s dominance in terms of model/segment and factory footprint.
“Cars don’t ship like iPhones, and there are benefits in high localization,” wrote the Morgan Stanley analysts.
In China, over 90% of Tesla’s parts are now being sourced from domestic companies. This should help Tesla China optimize its work even further, allowing Gigafactory Shanghai to play an ever-growing role in the company’s overall operations.
As for Gigafactory Texas and the Freemont, CA factory, Tesla has a similar goal of sourcing over 90% of parts and raw materials from North America, which includes the US, Mexico and Canada.
Further supply chain improvements are likely to include co-locating battery production at Gigafactory locations and self-manufacturing of chips, similar to what Apple has done with semiconductors.
Supply chain risks and disruptions are not diminishing and the best way to mitigate these risks is implementation of localization strategies.
https://www.teslarati.com/tesla-tsla-expansion-drivers-morgan-stanley/
Massive Push By USA To Strengthen Critical Supply Chains
A new report totaling several hundred pages, that supports localization and reshoring was released today, recommending immediate and far-reaching action on supply chains involving areas critical to the U.S. economy: large capacity lithium batteries, rare earth minerals, semiconductors and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Large capacity lithium batteries: The Department of Energy is aiming to release a 10-year plan to develop a domestic lithium battery supply chain capable of producing the batteries that power electric vehicles. The agency’s Advanced Technology Vehicles Manufacturing Loan Program will distribute $17 billion in an effort to support new research and manufacturing efforts in the United States.
Rare earth minerals: The Department of Interior will lead a task force to identify sites where critical minerals could be produced and processed in the United States.” The report said the U.S. will develop the capacity for “sustainable production, refining, and recycling” of the 17 rare earth metals used in cellphones, cars and magnets, while meeting high environmental standards.
Semiconductors: As the nation grapples with a chip shortage that has idled major auto manufacturing plants, the White House said it will work with the private sector to increase supply-chain transparency.
Advanced pharmaceutical ingredients: The Department of Health and Human Services will use authority granted under the Defense Production Act to commit approximately $60 million to “develop novel platform technologies to increase domestic manufacturing capacity for API.”
The recommendations support increased investments, vast improvements to supply chains and less reliance on other countries for crucial goods.

Southwest The Best For US Manufacturing Growth – Cranes Everywhere!
The Southwest U.S. increased its manufacturing output more than any other region in the U.S. in the four years through 2020, according to an analysis by The Wall Street Journal of data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
This area added more than 100,000 manufacturing jobs from January 2017 to January 2020, representing 30% of U.S. job growth in that sector and at roughly triple the national growth rate, according to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Some of the companies creating new manufacturing facilities in this region include: Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC), Tesla, Intel, Lucid Motors, Steel Dynamics, SpaceX, Pegatron, Haas Automation and Benchmark Electronics.
Contact Us

